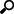Glossary
The difference between the position of a 3D point when it is projected back onto the 2D image plane, and the 2D detection in that plane.
3D point
The path though space that a moving marker follows. This reconstructed data is stored in a file as a time-series of points.
.pico file
Capture file that contains video data from a single camera and information about the logger at the point of capture.
An XML file, which contains the specified calibration parameters and threshold data for Vicon cameras. An .xcp file is created during the calibration process and is used when processing data from the cameras.
Blobs
Continuous areas of above-threshold data from the cameras. They are submitted as candidates to Vicon circle-fitting algorithms to determine which are likely to represent markers. Preview blobs are rendered as green rings around potential blobs.
Bundle
Using the currently available information, an attempt by Vicon CaraPost to minimize the output error for all cameras by adjusting current values. These may include camera internal data (such as focal length, etc) and external information (such as relationship to other cameras), and blob positions.
Caddy
Set of two cameras on a single arm of a Vicon Cara head rig.
A known pattern of markers that is used to calculate the positions of the cameras. The Vicon Cara system is supplied with a default calibration brim. If required, you can modify the calibration brim, using a template available from Vicon.
Calibration file
See .xcp file.
Calibration grid
A rigid device with a pattern of black blobs on a white background, used by Vicon CaraLive for alignment of cameras for initialization and frame-by-frame calibration.
Camera rays
See Rays.
Capture
See Take.
Onscreen display of view from Vicon camera. Vicon CaraPost enables you to display up to four rectangular views, labeled Channels 0, 1, 2 and 3. These views enable you to preview takes during processing.
See Camera view.
Commuter licensing
Temporarily moving a seat from a network license to a machine that is not connected to the license server network. This enables you to temporarily use Vicon software on a machine unconnected to the network that contains the license server.
Connected projections
Projections that have an associated detection or target track in the current camera view. A connected projection is rendered as a yellow cross within a circle.

Representations of blobs (markers) found in an image. When not selected, they are red circles (or ellipses) with a cross in the middle.

The cross represents the center point, which is used as the 2D coordinate of the detection. The red circle or ellipse represents the boundary of the blob (marker) and is used as part of the blob detection process.
The moving of a camera along a horizontal axis closer to or further from the subject.
Error
The difference between the center point of a projection and its associated (connected) detection or target track in that channel. It is often called the reprojection error. In Vicon CaraPost, it is displayed as a yellow line. The following image shows the center of a detection and a projection, with a yellow line (error) connecting the two.

Headbar
See Calibration brim.
Interpolation
The process by which Vicon CaraLive fills a gap in a reconstruction by calculating a smooth curve between two disconnected points. See also Reconstruction.
Marker
A circle painted on, drawn on, or stuck to an actor; or a sphere, hemisphere or disk coated with highly retroreflective material attached to an actor, whose motion is captured by a Vicon system. Vicon systems capture information from the markers and convert it into images that represent the position and radius of the marker.
Noise
Random background interference that is unrelated to the data being captured, causing random spikes, wobbles or jitters in motion data. Some noise is generally present in most data collected and may be caused by a number of factors. Vicon CaraPost offers a number of tools and techniques to help eliminate noise.
Occlusion
The obstruction of a marker from the view of one or more cameras. Occlusion is generally caused by a marker being covered by a body part or another motion capture subject.
The rotation of a stationary camera in a horizontal plane about a vertical axis. See also Dolly and Truck.
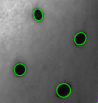
Points
Collections of blob detections and\or target tracks as well as projections. When not selected they are blue rings that match up with the boundary of the detection with which they are associated.

If the point is a target track keyframe, it is rendered as a blue box representing the pattern area, and a broken yellow circle representing the middle of the pattern area.
If the point is a target track but not on a keyframe, it will be rendered as a broken blue circle representing the center of the pattern area.
Projections
(or Reprojections) See Reconstruction.
Lines from points in the 3D world back to the corresponding points in each camera imaging plane.
The process by which Vicon software calculates the position of markers in 3D space and links these points frame-by-frame. This reconstructed data is stored in a file as a time-series of points. 3D points that are calculated from the corresponding 2D image points are known as reconstructions. See also 2D reconstruction error.
Scrub
The movement of the current time cursor left or right along the timebar.
Sensor
Camera component that detects light and converts it into an electronic signal, enabling the 2D positions of markers to be recorded over time.
Sequence
See Take.
The stabilization error is a weighted sum of the following errors:
Base Frame Stabilization Error The root-mean-square of the differences between the percentage specified by the Stable Points Percent most stable points in each frame and the corresponding points in the base frame (calculated across the whole of the Active Range).
Inter Frame Stabilization Error The root-mean-square of the differences between the percentage specified by the Stable Points Percent most stable points in each frame and the previous frame (calculated across the whole of the Active Range).
A recording of motion data with a Vicon system, using markers painted on or attached to the subject of the recording (normally an actor). Also known as a capture or sequence.
Target tracking uses pattern matching to calculate tracks.The target tracker tracks the center of the marker.
The blue box contains the pattern that you are tracking (the marker) and should be adjusted to comfortably contain the marker. The green cross represents the comparison region, which is the area in adjacent frames that will be searched to find the pattern that is being matched (ie the marker). The green circle represents the middle of the pattern.
The moving of a camera side-to-side along a horizontal axis. See also Dolly and Pan.
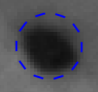
Unconnected projections
Projections that do not have an associated detection or target track in the current camera view. Unconnected projections are rendered as orange x signs surrounded by a circle. See also Detections and Target track.